What is operator ?
Operators are the symbols or the instructions that is used to tell the compiler for which type of operation to be performed in the program. The operators are used for mathemetical and logical manipulations.
Types of operators in C++ are :
- Arithmetic Operators
- Assignment Operators
- Increment and Decrement Operator
- Relational Operators
- Logical Operators
- Conditional operator
- Sizeof Operator
- Bitwise Operators
- Other Operators
1. Arithmetic operators :
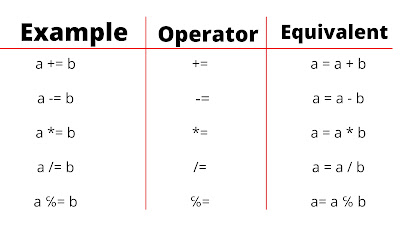
a) Addition : It is used to do addition between two or more operands in a program. The addition is denoted using the ' + ' sign.
For example : a + b
b) Substraction: It is used to do substraction between two or more operands in a program. The substraction is denoted using the ' - ' sign.
For example : a - b
c) Multiplication : It is used to do multiplication between two or more operands in a program. The multiplication is denoted using the ' * ' sign.
For example : a * b
d) Division : It is used to do division between two operands in a program. The division is denoted using the ' / ' sign.
For example : a / b
e) Modulus : It is used to compute the remainder of the given operands in a program. The modulus is denoted using the ' % ' sign.
For example : a % b
2. Assignment operators :
3. Increment and Decrement operator :
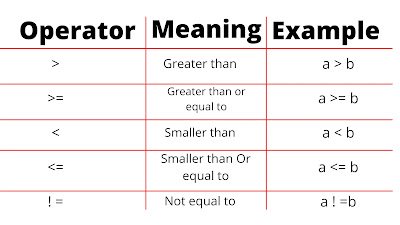
4. Relational Operators:
5. Logical Operators :
The Logical Operators are used for testing or checking more then one condition and making the decisions according to it.
- && - It is the condition in which both the condition should satisfy, if in case one condition is also false then it will return 0.
- | | - It is known as OR operator. In this condition, at least one condition should satisfy otherwise it will return 0.
- != - It is known as NOT operator. In this case, if the condition is false it will return 0.
6. Conditional operator :
It is also known as the ternary operator because it works on three expression as operands. The first expression is the given condition, which will be tested and if the condition is true then the second expression is executed or else the third condition will be executed.
7. Sizeof operator :
8. Bitwise operators :








2 Comments
Best
ReplyDeleteVery helpful
ReplyDelete